Partials#
In Talkable, Liquid partials are reusable snippets of code that can be included in main template. This allows for modular and maintainable template design.
Adding a Partial#
To add a new Liquid partial, follow these steps:
Navigate to the Partials modal: Navigate to the HTML & CSS section of the Editor. Click on the Partials button.
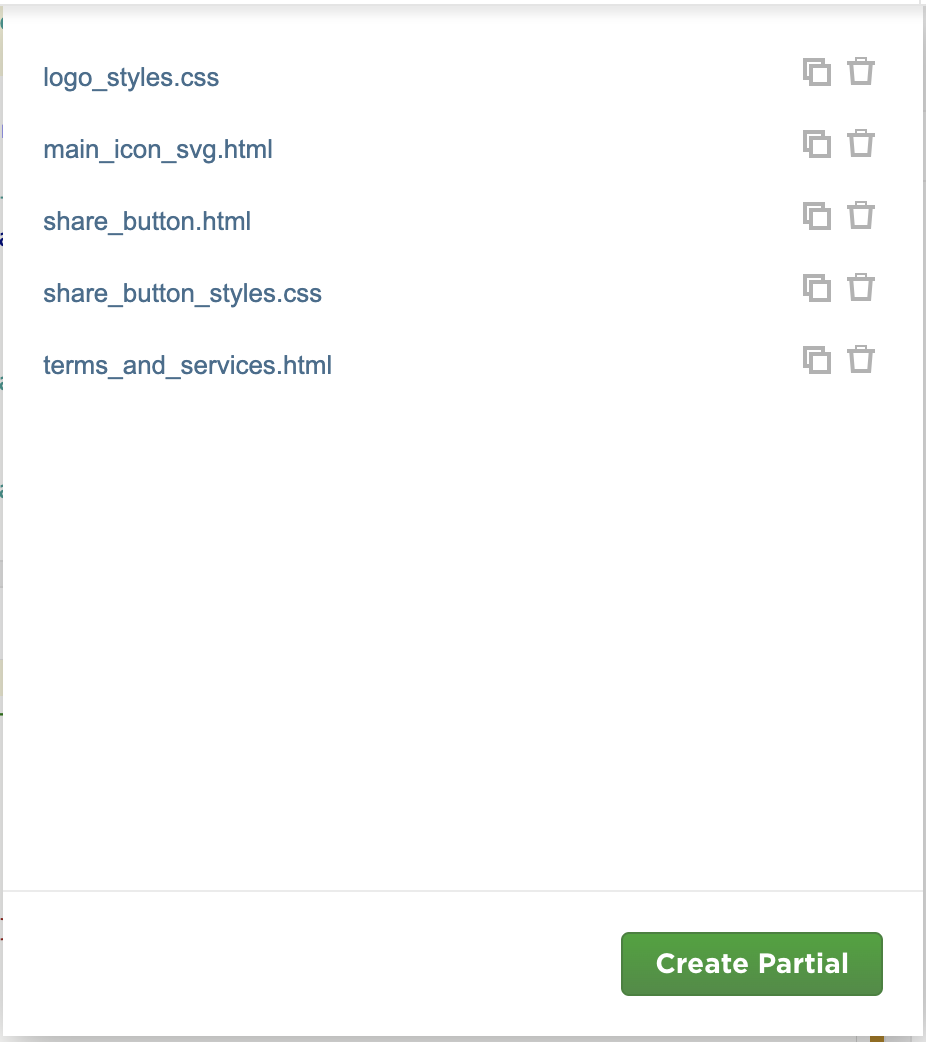
Create a Partial: Click on the Create Partial button. This will open a new form where you can define your partial.
Name: Provide a unique name for your partial. This name will be used to reference the partial in your main templates. The name could be separated by underscores.
Type: Select the type of content you want to include in your partial. This can be either HTML or CSS. The content of the partial will be rendered as HTML or CSS based on the type you select.
Insert to current position: This option will insert the partial at the current cursor position in the editor.
Including a Partial in a Main Template#
To include a partial in a main template, use the name of the partial you created. The syntax for including a partial is as follows:
{% render 'partial_name' %}
Replace partial_name with the actual name of your partial. This will insert the content of the partial at the specified location in your main template.
Example#
Here is an example of how to create and use a Liquid partial:
Create a Partial:
Name: header
Type: HTML
Content:
<header> <h1>{{ site.title }}</h1> </header>
Render the Partial in a Main Template:
<body> {% render 'header' %} <main> {{ content }} </main> </body>
Variables assigned using variable tags can be passed to a template by listing them as parameters on the render tag:
{% assign my_variable = 'apples' %} {% render 'header', my_variable: my_variable, my_other_variable: 'oranges' %}
Note
The code within the rendered template does not automatically have access to the variables assigned using variable tags within the parent template. Similarly, variables assigned within the rendered template cannot be accessed by code in any other template.
By following these steps, you can efficiently manage reusable components within your Liquid templates, enhancing both modularity and maintainability.
See also